COVID-19 Research & AI-Driven Solutions
Computational Intelligence for Pandemic Modeling, Diagnosis, and Healthcare Optimization
Project Overview
In this project, we applied advanced computational intelligence and AI to address critical challenges in biomedical engineering and public health, with a strong emphasis on the COVID-19 pandemic. We developed diverse models to diagnose the virus from lung X-rays using CNNs, estimate its pandemic spread, and analyze its relationship with climatological and solar factors. Our work also extended to healthcare logistics, using hybrid algorithms to schedule nurses, and assessing the impact of pre-infection statin use on virus severity. This complements our broader research in using deep learning for medical image analysis, including segmenting tumors and diagnosing biomechanical issues.
AI Diagnosis
CNN-based Detection
Pandemic Modeling
Spread Estimation & Forecasting
Climatology Analysis
Environmental Factors
Research Visualization

Climatological Parameters Impact on COVID-19 Outbreak
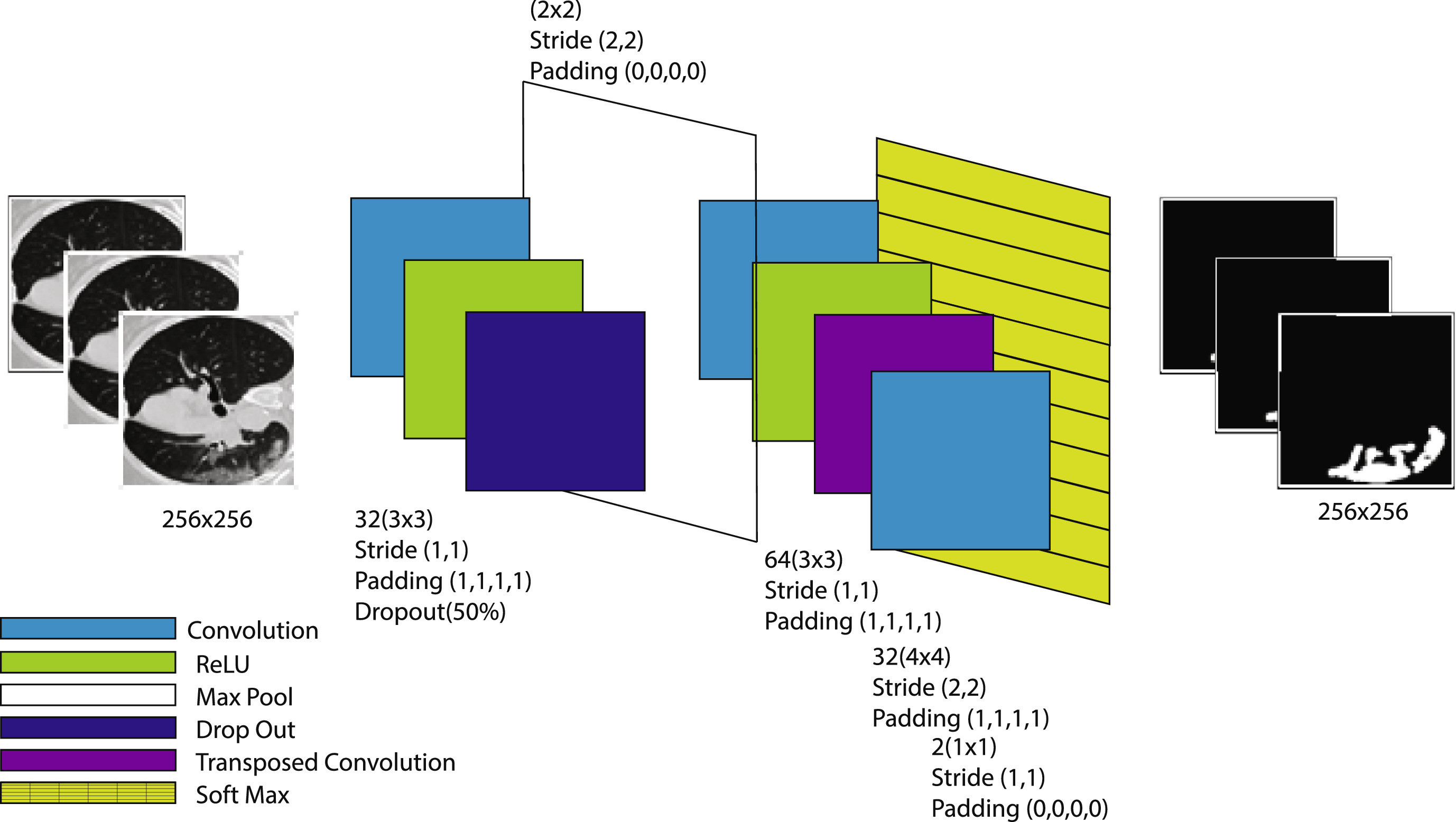
AI-Powered Diagnosis from Lung X-ray Images
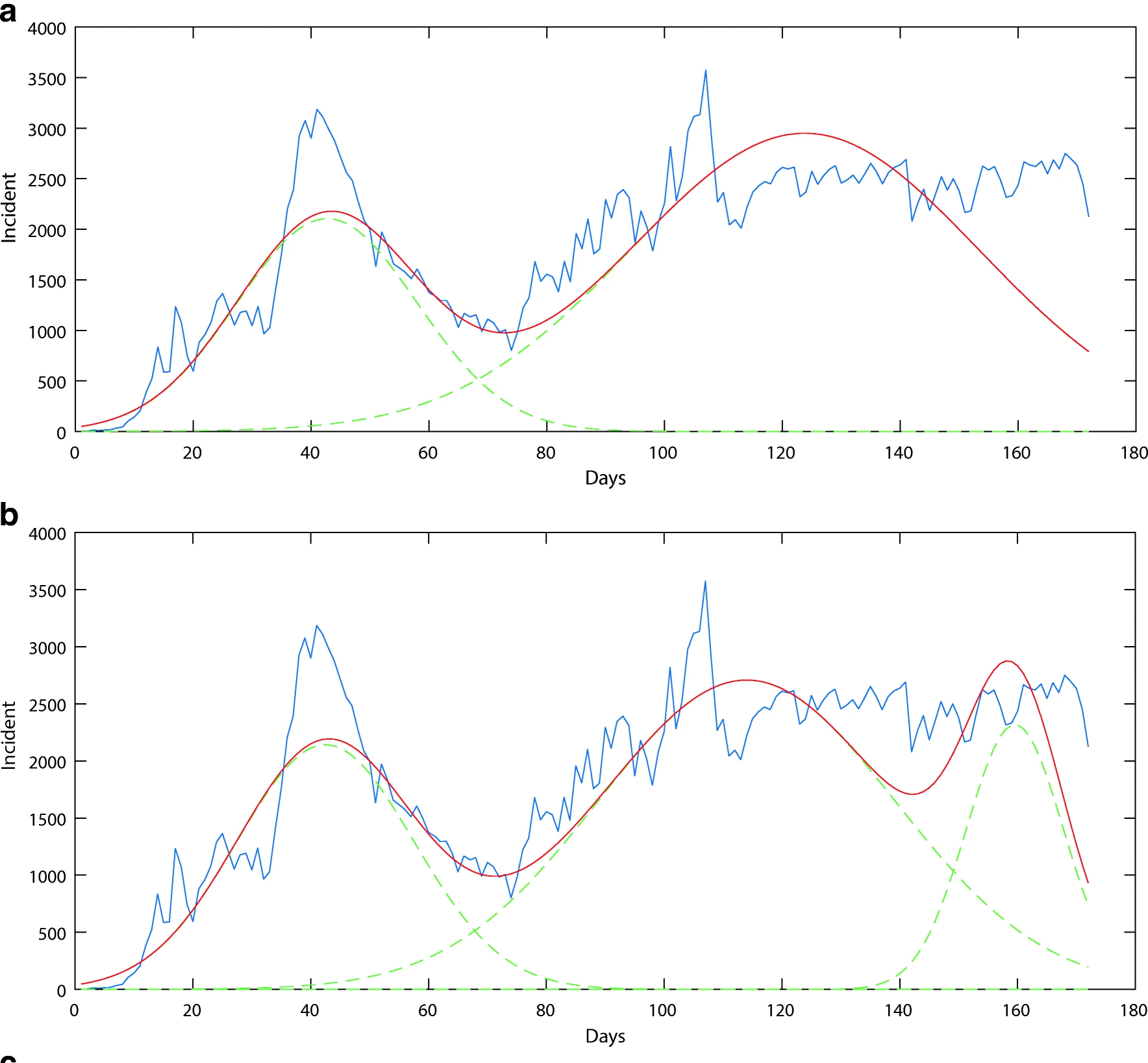
Sub-Epidemic Model for Pandemic Estimation
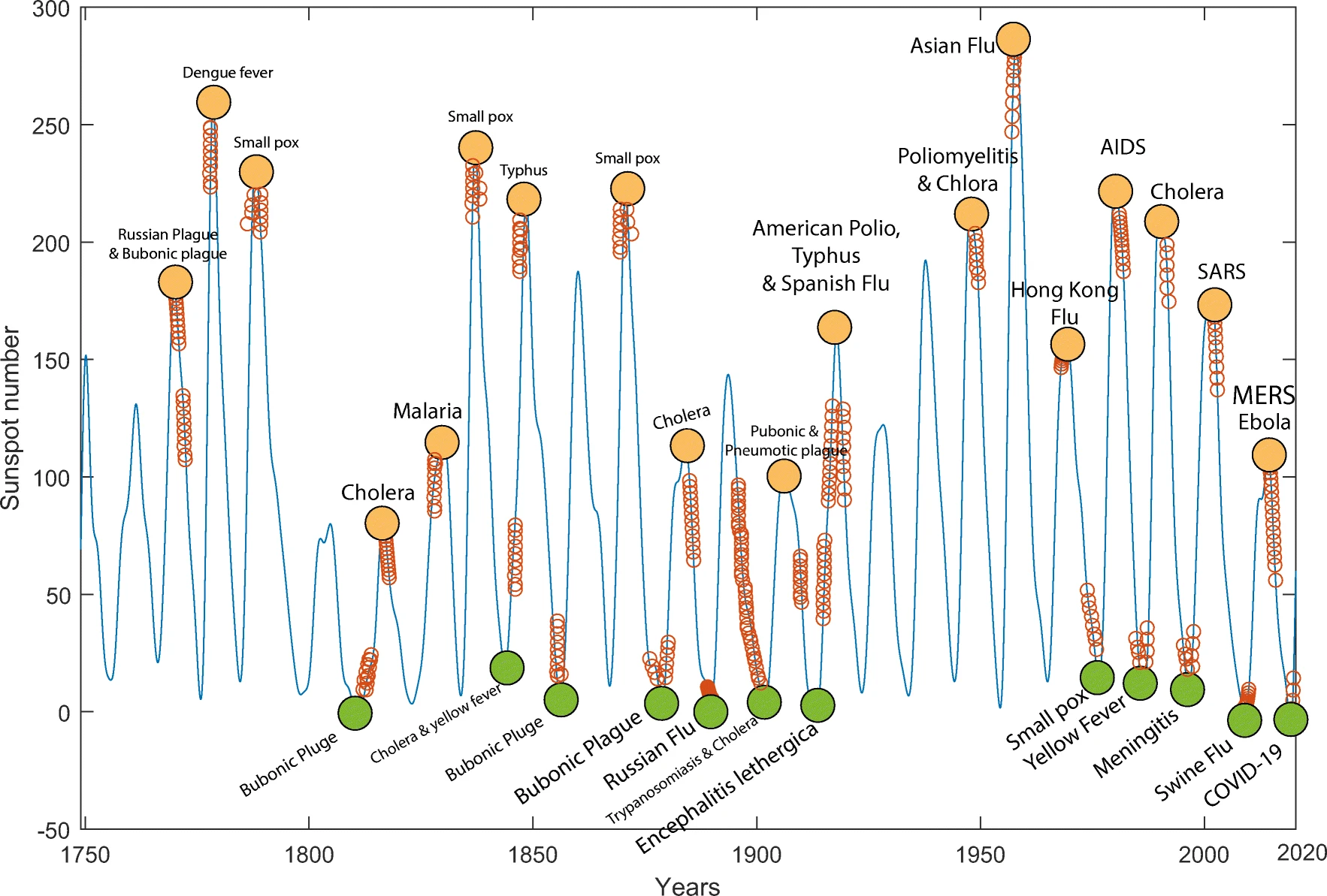
Solar Activity and Future Virus Forecasting
Key Research Areas
AI-Based Diagnosis
Development of convolutional neural networks for detecting and diagnosing infected tissue in COVID-19 patients from lung X-ray images with high accuracy and sensitivity.
Climatology Investigation
Investigation of effective climatological parameters including temperature, humidity, and air quality on COVID-19 outbreak patterns and transmission rates.
Pandemic Modeling
Development of sub-epidemic models for estimating COVID-19 pandemic spread and assessment of travel-related risks using advanced forecasting techniques.
Healthcare Logistics
Novel hybrid salp swarm and genetic algorithm (HSSAGA) for optimizing nurse scheduling and resource allocation in COVID-19 patient care.
Solar Activity Analysis
Multi-step autoregression (MSAR) analysis revealing relationships between solar activity and COVID-19 spread, with forecasting of possible future viruses.
Medical Treatment Analysis
Machine learning study on the effect of pre-infection statin use in reducing COVID-19 severity and improving patient outcomes.
Post-Pandemic Impact
Analysis of artificial intelligence and digital transformation impact on industry and energy sectors in the post-COVID-19 era.
Related Publications
Investigation of Effective Climatology Parameters on COVID-19 Outbreak in Iran
Ahmadi, M., Sharifi, A., Dorosti, S., Ghoushchi, S. J., & Ghanbari, N.
Science of the Total Environment, 729, 138705, 2020
Diagnosis and Detection of Infected Tissue of COVID-19 Patients Based on Lung X-Ray Image Using Convolutional Neural Network Approaches
Hassantabar, S., Ahmadi, M., & Sharifi, A.
Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 140, 110170, 2020
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Digital Style on Industry and Energy Post-COVID-19 Pandemic
Sharifi, A., Ahmadi, M., & Ala, A.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(34), 46964-46984, 2021
HSSAGA: Designation and Scheduling of Nurses for Taking Care of COVID-19 Patients Using Novel Method of Hybrid Salp Swarm Algorithm and Genetic Algorithm
Abadi, M. Q. H., Rahmati, S., Sharifi, A., & Ahmadi, M.
Applied Soft Computing, 108, 107449, 2021
Revealing the Relationship Between Solar Activity and COVID-19 and Forecasting of Possible Future Viruses Using Multi-Step Autoregression (MSAR)
Nasirpour, M. H., Sharifi, A., Ahmadi, M., & Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(28), 38074-38084, 2021
Presentation of a Developed Sub-Epidemic Model for Estimation of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Assessment of Travel-Related Risks in Iran
Ahmadi, M., Sharifi, A., & Khalili, S.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(12), 14521-14529, 2021
Studying the Effect of Taking Statins Before Infection in the Severity Reduction of COVID‐19 with Machine Learning
Davoudi, A., Ahmadi, M., Sharifi, A., Hassantabar, R., Najafi, N., Tayebi, A., ... & Rabiee, M.
BioMed Research International, 2021(1), 9995073, 2021